
Therapeutic Botox, also known as medical Botox or botulinum toxin therapy, is a medical treatment that uses a purified form of the botulinum toxin to address various medical conditions and alleviate symptoms. While botulinum toxin is widely known for its cosmetic applications to reduce wrinkles and fine lines, therapeutic botulinum toxin serves a different purpose by targeting specific medical conditions.
Use of Therapeutic Botulinum Toxin at Northwest Neurological
Muscle Spasms: Botulinum toxin can be injected into muscles to treat conditions like cervical dystonia (a painful neck muscle spasm), blepharospasm (involuntary eyelid twitching), and limb spasticity.
Chronic Migraines: Botulinum toxin is an FDA-approved treatment for chronic migraines. It is administered as multiple injections into the head and neck muscles to reduce the frequency and severity of migraine headaches.
Hyperhidrosis: Botulinum toxin can be used to treat excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis) by blocking the sweat glands’ activity in the affected area, such as the armpits, palms, or soles of the feet.
*Botulinum toxin is not FDA-approved for all spasms including post-traumatic spasm, isolated neck pain without involuntary movement, TMJ pain, etc.)
Botulinum Toxin
A neurotoxin produced by the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. It is highly potent and can temporarily block nerve signals and muscle contractions when administered in small, targeted, controlled doses.
Mechanism of Action: Botulinum toxin works by blocking the release of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that signals muscles to contract. When acetylcholine release is inhibited, muscle contractions are temporarily reduced or eliminated, leading to symptom relief in the treated condition.
Treatment Process: Therapeutic botulinum toxin is administered through injections by a qualified healthcare professional, such as a neurologist, dermatologist, Nurse Practitioner or RN, depending on the condition being treated. The injections are typically done in a clinical setting and may require multiple sessions over time for the best results.
Duration of Effects: The effects of therapeutic botulinum toxin are temporary and typically last for several months, depending on the condition being treated. Patients may need repeat injections to maintain symptom relief.
Safety: When administered by a trained and experienced medical professional, therapeutic botulinum toxin is generally considered safe. However, like any medical procedure, it can have side effects, including muscle weakness, pain at the injection site, and, rarely, more serious complications. The dosage and injection technique are crucial in minimizing these risks.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare provider to determine if therapeutic botulinum toxin is a suitable treatment option for your specific medical condition. They can assess your individual needs, discuss potential risks and benefits, and create a personalized treatment plan if botulinum toxin therapy is deemed appropriate.
Types of botulinum toxin type A (BoNT-A) are commonly used for various therapeutic and cosmetic applications. Several different brands and formulations of BoNT-A are available, each with its unique properties and characteristics. Here are some of the well-known types of BoNT-A:
OnabotulinumtoxinA (Botox):
Botox is one of the most recognized and widely used brands of BoNT-A.
It is used for both therapeutic and cosmetic purposes.
Botox is commonly employed to treat conditions such as spasticity, chronic migraines, overactive bladder, and to reduce the appearance of facial wrinkles and lines.
AbobotulinumtoxinA (Dysport):
Dysport is another BoNT-A product approved for both therapeutic and cosmetic uses.
It is often used to treat conditions like cervical dystonia and is also used for cosmetic purposes to reduce wrinkles.
IncobotulinumtoxinA (Xeomin):
Xeomin is a BoNT-A product that contains only the active toxin without additional proteins.
It is used for therapeutic purposes, including the treatment of spasticity and cervical dystonia.
*It shows benefit for use in migraines, but it is not FDA-approved for this indication and insurance may not cover.
*Xeomin is also used for cosmetic applications to reduce the appearance of wrinkles.
These various BoNT-A formulations have subtle differences in terms of onset of action, duration of effect, and potential side effects. The choice of which BoNT-A product to use depends on the specific medical or cosmetic condition being treated and individual patient preferences.
When considering BoNT-A treatment, it’s essential to consult with a qualified healthcare provider. They can assess your needs, discuss the available options, and recommend the most appropriate BoNT-A type and product for your specific goals and medical history.
Chronic migraine treatment with one type of botulinum toxin, also known as onabotulinumtoxinA (Botox®), is an FDA-approved therapy designed to reduce the frequency and severity of migraine headaches in individuals who experience chronic migraines. Chronic migraines are defined as headaches occurring on 15 or more days per month for at least three months, with at least eight of those headaches being migraines.
Here’s how chronic migraine treatment with botulinum toxin works:
Consultation: The process typically begins with a consultation with a healthcare provider, often a neurologist or headache specialist. They will assess your medical history, migraine patterns, and the severity of your symptoms to determine if you are a suitable candidate for botulinum toxin treatment.
Treatment Sessions: If you are a candidate, you will undergo a series of botulinum toxin treatment sessions. The treatment involves injecting botulinum toxin into specific muscle areas around the head and neck, including the forehead, temples, back of the head, neck, and shoulders. These injections target muscles that may be contributing to migraine attacks by reducing muscle tension and the release of certain neurotransmitters. One session typically lasts somewhere between 10-15 minutes.
Procedure Frequency: Botulinum toxin for chronic migraines is typically administered every 12 weeks (approximately once every three months). Patients may require multiple sessions to experience the full benefits, and it can take a few treatment cycles to see significant improvements in migraine frequency and severity.
Effectiveness: Botulinum toxin treatment does not provide immediate relief from migraines. It may take a week or more for the effects to become noticeable. Studies have shown that botulinum toxin treatment can reduce the number of migraine days per month by up to 50% in some patients, but anecdotally some have had a near elimination of their headaches while receiving treatments.
Maintenance: To maintain the benefits of botulinum toxin treatment for chronic migraines, it is important to stick to the recommended treatment schedule and continue with the injections as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
Side Effects: Common side effects of botulinum toxin treatment for migraines may include temporary pain or discomfort at the injection sites, mild neck weakness, and, rarely, other side effects like eyelid drooping. These side effects are generally temporary and resolve on their own.
Safety: Botulinum toxin treatment for chronic migraines is considered safe when administered by a qualified healthcare provider. However, it may not be suitable for everyone, and your healthcare provider will assess your individual circumstances before recommending the treatment.
*It’s essential to have realistic expectations about the outcomes of botulinum toxin treatment for chronic migraines. While it can be highly effective for some individuals, it may not eliminate migraines entirely. Your healthcare provider will work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan and may consider other migraine management strategies in conjunction with botulinum toxin treatment, such as lifestyle modifications and medications.

The administration of botulinum toxin for chronic migraines involves multiple injections into specific muscles/areas of the head (scalp) and neck. These injections are typically performed by a qualified healthcare provider. The goal is to target muscles and nerve pathways that may contribute to migraine headaches.
Here are the general areas where botulinum toxin injections are commonly administered for migraine treatment:
Forehead: Injections are given across the forehead, typically in the frontalis muscle, to reduce tension and muscle contractions that can trigger migraines.
Temples: Injections are placed in the temporal region for tension-related migraines.
Neck: Injections are administered to the occipital area (back of the head) and the suboccipital muscles. These injections aim to relax the muscles in the neck and upper back, which may contribute to migraines.
Upper back: In some cases, injections are given to the trapezius muscles in the shoulders. These muscles can become tense and contribute to headache symptoms.
Upper Neck: Injections may be placed in the cervical paraspinal muscles, which are located along the sides of the neck and upper spine.
Other Sites: Depending on the individual’s migraine patterns and symptoms, additional injections may be administered in other areas of the head and neck as determined by the healthcare provider.
*This is not FDA-approved and may limit reimbursement by your insurance.
The injections themselves are relatively quick and typically involve multiple small injections in each targeted area. Some patients may experience mild discomfort or a brief stinging sensation during the procedure, but it is generally well-tolerated. Afterward, there may be some temporary redness or swelling at the injection sites.
It’s important to note that botulinum toxin treatment for migraines is typically administered every 12 weeks (approximately once every three months). The full effects may take some time to become noticeable, and patients often require multiple treatment cycles to experience significant reductions in migraine frequency and severity.
If you are considering botulinum toxin treatment for chronic migraines, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider who specializes in migraine management. They will assess your specific migraine pattern and determine the most appropriate injection sites and dosage for your condition.
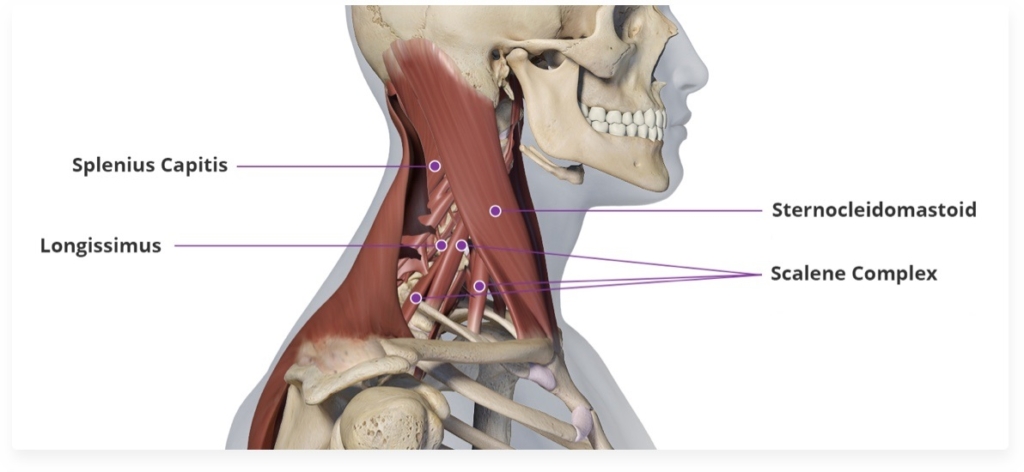
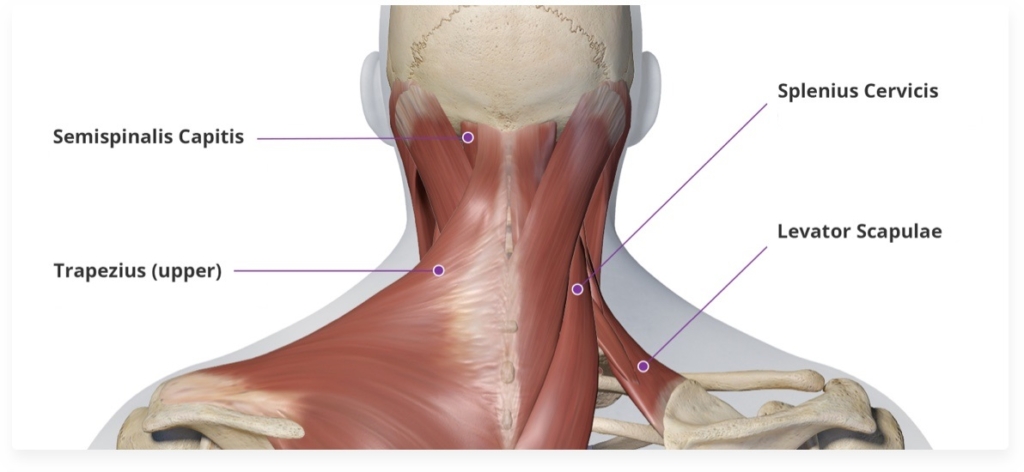
Botulinum toxin injections are a common and effective treatment for cervical dystonia, a neurological disorder characterized by involuntary muscle contractions or spasms in the neck and shoulder region.
These injections aim to relax the overactive muscles responsible for the abnormal movements and positions of the head and neck.
Here’s what you can expect during botulinum toxin treatment for cervical dystonia:
Consultation: The process begins with a consultation with a neurologist or movement disorder specialist. During this appointment, the healthcare provider will evaluate your medical history, the severity of your cervical dystonia symptoms, and assess your specific muscle involvement.
Injection Sites: The healthcare provider will identify the specific muscles contributing to your cervical dystonia symptoms. Commonly targeted muscles include the sternocleidomastoid, trapezius, and other muscles in the neck and shoulder area.
Preparation: The skin over the injection sites is cleaned with an antiseptic solution. In some cases, a topical anesthetic or ice pack may be applied to numb the area before the injections to minimize discomfort.
Injections: Botulinum toxin is administered via a fine needle directly into the affected muscles. The number of injections and the amount of botulinum toxin used will vary depending on the severity and distribution of your symptoms.
Discomfort: Some patients may experience mild discomfort during the injections, but the procedure is generally well-tolerated.
Duration: The effects of botulinum toxin injections for cervical dystonia are not immediate. It may take several days to a week or more for the full effects to become noticeable.
Repeat Injections: Botulinum toxin treatment for cervical dystonia is typically administered every 12 weeks (approximately once every three months). Over time, you and your healthcare provider will determine the appropriate dosage and injection sites to achieve the best results.
Side Effects: Common side effects of botulinum toxin injections for cervical dystonia may include temporary weakness or discomfort at the injection sites. Some patients may also experience neck pain, headache, or mild difficulty swallowing. These side effects are generally temporary and resolve on their own.
Improvement: Botulinum toxin injections can significantly improve the symptoms of cervical dystonia, such as head turning, tilting, or other abnormal head positions, by reducing muscle spasms and increasing head stability.
Maintenance: To maintain the benefits of botulinum toxin treatment, it’s crucial to adhere to the recommended treatment schedule and continue with regular injections as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
*It’s essential to work closely with a healthcare provider experienced in treating cervical dystonia with Botulinum toxin to receive the most effective and safe treatment. They will customize the treatment plan to address your specific needs and symptoms, ensuring the best possible outcome in managing this condition.
Botulinum toxin injections are a commonly used and effective treatment for blepharospasm, a neurological condition characterized by involuntary and excessive blinking or spasms of the eyelids. These injections help to relax the overactive muscles responsible for the uncontrolled eye movements and can provide relief from the symptoms.
Here’s what you can expect during botulinum toxin treatment for blepharospasm:
Consultation: The process begins with a consultation with a neurologist or ophthalmologist who specializes in the treatment of blepharospasm. During this appointment, the healthcare provider will evaluate your medical history, the severity of your symptoms, and assess your specific muscle involvement.
Injection Sites: The healthcare provider will identify the specific muscles responsible for your blepharospasm symptoms. In most cases, the injections are administered into the orbicularis oculi muscles, which are the muscles that surround the eyes and control blinking.
Preparation: The skin around the eyes is cleaned with an antiseptic solution. In some cases, a topical anesthetic or a cold pack may be applied to numb the area slightly before the injections to minimize discomfort.
Injections: Botulinum toxin is administered via a fine needle directly into the affected muscles around the eyes. The number of injections and the amount of botulinum toxin used will depend on the severity and distribution of your symptoms.
Discomfort: Most patients experience minimal discomfort during the injections, and the procedure is usually well-tolerated.
Duration: The effects of botulinum toxin injections for blepharospasm are not immediate. It may take several days to a week or more for the full effects to become noticeable.
Repeat Injections: Botulinum toxin treatment for blepharospasm is typically administered every 12 weeks (approximately once every three months). The frequency of injections may vary depending on the individual’s response and the severity of symptoms.
Side Effects: Common side effects of botulinum toxin injections for blepharospasm may include temporary eyelid drooping, redness, bruising, or discomfort at the injection sites. These side effects are generally temporary and resolve on their own.
Improvement: Botulinum toxin injections can significantly improve the symptoms of blepharospasm by reducing the frequency and intensity of eyelid spasms, allowing for more normal eye function.
Maintenance: To maintain the benefits of botulinum toxin treatment, it is essential to follow the recommended treatment schedule and continue with regular injections as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
*Working closely with a healthcare provider experienced in treating blepharospasm with botulinum toxin is crucial to receive the most effective and safe treatment. They will tailor the treatment plan to address your specific needs and symptoms, ensuring the best possible outcome for managing this condition.
 Botulinum toxin injections are an effective treatment option for hyperhidrosis, a condition characterized by excessive sweating. The injections can provide relief by temporarily blocking the signals that stimulate the sweat glands. Here’s what you can expect during botulinum toxin treatment for hyperhidrosis:
Botulinum toxin injections are an effective treatment option for hyperhidrosis, a condition characterized by excessive sweating. The injections can provide relief by temporarily blocking the signals that stimulate the sweat glands. Here’s what you can expect during botulinum toxin treatment for hyperhidrosis:
Consultation: The process typically begins with a consultation with a dermatologist or a healthcare provider who specializes in treating hyperhidrosis. During this appointment, the healthcare provider will assess the severity of your sweating, your medical history, and any underlying causes.
Determination of Injection Sites: The healthcare provider will identify the specific areas where you experience excessive sweating. Commonly treated areas include the underarms (axillary hyperhidrosis), palms of the hands (palmar hyperhidrosis), and soles of the feet (plantar hyperhidrosis).
Preparation: The skin in the treatment area is cleaned and dried thoroughly. In some cases, a topical anesthetic may be applied to minimize discomfort during the injections, but this is less common for hyperhidrosis treatment.
Injections: Botulinum toxin is administered using a very fine needle directly into the sweat glands in the affected area. The injection process is relatively quick and generally well-tolerated.
Discomfort: Many patients experience minimal discomfort during the injections. The use of very fine needles and the small amounts of botulinum toxin used usually make the procedure relatively painless.
Duration: The effects of botulinum toxin injections for hyperhidrosis are not immediate, but you may start noticing reduced sweating within a few days. The full effects typically become more noticeable within a couple of weeks.
Duration of Effect: Botulinum toxin treatment for hyperhidrosis provides relief that can last for several months, often around six to nine months on average. The duration of the effect may vary from person to person.
Repeat Injections: To maintain the benefits of botulinum toxin treatment for hyperhidrosis, you will need to repeat the injections as the effects wear off. The frequency of injections may vary, but they are typically done when sweating returns or becomes bothersome again.
Side Effects: Common side effects of botulinum toxin injections for hyperhidrosis may include temporary pain or discomfort at the injection sites, redness, or bruising. In rare cases, there may be mild weakness in nearby muscles, but this is usually transient and not a major concern for most individuals.
Improvement: Botulinum toxin injections can significantly reduce sweating in the treated areas, improving your quality of life and reducing the social and practical challenges associated with excessive sweating.
It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider experienced in treating hyperhidrosis with botulinum toxin to determine the most suitable treatment plan for your specific needs. They will customize the treatment by identifying the areas that require injections and tailoring the dosage to your individual condition.
